Last few months have seen a grotesque display of obscene wealth in India, a country with well-documented levels of extreme poverty, hunger and unemployment. Indian billionaire Mukesh Ambani has splurged hundreds of millions of dollars on his son's wedding attended by top politicians including Prime Minister Narendra Modi, Hollywood and Bollywood celebrities and Ambani's fellow billionaires who have accumulated vast amounts of wealth in one of the world's most unequal countries. Experts blame it on Mr. Modi's policies promoting crony capitalism. Viral Acharya, former deputy governor of Reserve Bank of India, told the BBC that their ability to acquire large distressed companies, a growing appetite for mergers and acquisitions, and India's conscious industrial policy of creating "national champions via preferential allocation of projects and in some cases regulatory agencies turning a blind eye to predatory pricing".
 |
| Indian Prime Minister Modi at the Ambani Wedding in Mumbai. Source: ANI |
Between 2014-15 and 2022-23 on Mr. Modi's watch, the rapid rise in inequality in India has been particularly striking in terms of wealth concentration, according to World Inequality Lab. The top 1% now control over 40% of total wealth in India, up from 12.5% in 1980, and they earn 22.6% of total pre-tax income, up from 7.3% in 1980. Almost 90% of the country's billionaire wealth has been found concentrated in the hands of the upper castes. The Inequality Report concludes: "This spectacular rise of inequality (in India) makes the “Billionaire Raj” headed by India’s modern bourgeoise more unequal than the British Raj headed by the colonialist forces. It also squarely places India among the most unequal countries in the world".
Bollywood, the powerful Indian film industry, has become a key enabler of BJP's billionaire-friendly and Islamophobic policies. In a piece titled “India's theatrical politics: Bollywood, billionaires and the BJP", authors Sehr Rushmeen and Wanya Sidhu write: "By shaping narratives that subtly endorse “Hindutva” ideologies, sometimes even employing Muslim actors to deliver skewed messages, Bollywood contributes to a socio-political echo chamber in favor of Modi’s BJP...... Bollywood movies transcend mere entertainment; they convey narratives cleverly crafted to align with the BJP’s political agenda. By consistently portraying Muslims and Pakistan in a negative spotlight, these Indian blockbusters perpetuate a cycle of fear and nationalistic fervor to garner votes for the BJP while discarding the imperative of forging national unity".
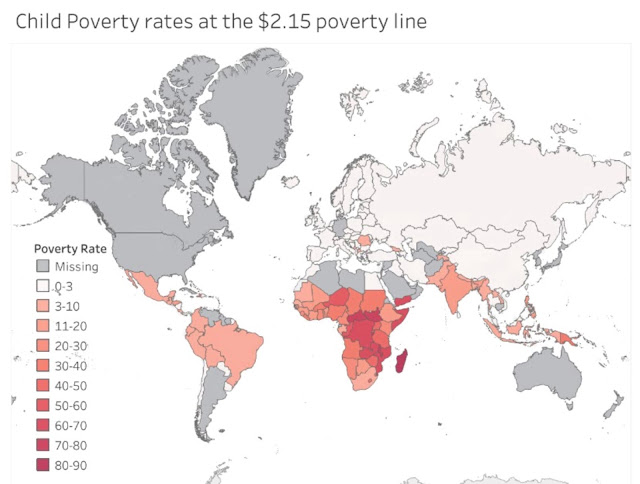
Meanwhile, India's child-wasting rate of 18.7% is the highest in the world, according to the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2023 released last year. The South Asian country’s child wasting rate is higher than that of war-torn Yemen (at 14.4%) and Sudan (at 13.7%), which are ranked second and third in the world. Pakistan's child wasting rate is 8%. It represents the share of children under age five who have low weight for their height, reflecting acute undernutrition. The child wasting rate of the South Asia region is 14.8%, the highest of any world region and more than twice the child wasting rate of Africa. India is home to a quarter of the world's most undernourished people. According to the United Nations, India has nearly 195 million undernourished people. This is more than any other country, including China.
 |
| India Tops in Child Wasting Rate. Source: The Wire |
 |
| India Tops the World in Child Wasting. Source: Global Hunger Index 2023 |
India's Hindu Nationalist government of Prime Minister Narendra Modi wants to project India as a superpower launching moon missions and hosting G20 summits. Since the GHI 2023 report runs counter to this PR exercise, New Delhi has rejected its findings. But its own National Family Health Survey 5 (NFHS 5) says that "Thirty-six percent of children under age five years are stunted; 19 percent are wasted; 32 percent are underweight; and 3 percent are overweight. Children born to mothers with no schooling and children in the lowest wealth quintile are most likely to be undernourished".
Overall, India ranks at the 111th position out of 124 countries, with neighboring Pakistan (102nd), Bangladesh (81st), Nepal (69th) and Sri Lanka (60th) faring better than India in the index. India has slipped four notches from its 107th position in 2022.
India has slipped 4 places, from 107 in 2022 to 111 in 2023, on GHI. Pakistan's ranking has also slipped 3 places, from 99 to 102. It is not a huge surprise since the country is still facing the aftermath of the disastrous floods of 2022. It is also suffering from a serious economic crisis. Meanwhile, India's Modi government is making claims to being the world's fastest growing economy. And yet, Indian children are the most malnourished in the world.
 |
| India Malnutrition Indicator Trends. Source GHI 2023 |
 | |
|
There's a close relationship between hunger and poverty. At the $3.65 poverty line, India accounts for 40% of the slight upward revision of the global poverty rate from 23.6% to 24.1%, according to the World Bank September 2023 Global Poverty Update. It is the same update that made the following recent headline in the Indian and Pakistani media about Pakistan: "Pakistan's 40% Population Lives Below Poverty Line, Says World Bank". Fact: 45.9% of Indians and 39.4% of Pakistanis live below the $3.65 a day poverty line as of September, 2023, according to the latest World Bank global poverty update that takes into account the impact of inflation on poverty rates. But neither the Pakistani media nor India's compliant "Godi Media" reported it. Nor did they question why poverty in India is growing despite the Modi government's claim to be "the world's fastest growing economy".
Related Links:
Haq's Musings
South Asia Investor Review
Pakistan Among World's Largest Food Producers
Food in Pakistan 2nd Cheapest in the World
India in Crisis: Unemployment and Hunger Persist After COVID
India Rising, Pakistan Collapsing
Record Number of Indians Seeking Asylum in US
Vast Majority of Pakistanis Support Imran Khan's Handling of Covid19 Crisis
Incomes of Poorest Pakistanis Growing Faster Than Their Richest Counterparts
Pakistanis Consuming More Calories, Fruits & Vegetables Per Capita
How Grim is Pakistan's Social Sector Progress?
Pakistan Fares Marginally Better Than India On Disease Burdens
COVID Lockdown Decimates India's Middle Class
Pakistan Child Health Indicators
Pakistan's Balance of Payments Crisis
How Has India Built Large Forex Reserves Despite Perennial Trade Deficits
Riaz Haq's Youtube Channel